命令模式
是什么?
先举个生活中的例子阐述命令模式。平时我们去银行办业务,快餐厅吃饭,有时因为人数多,资源有限等原因,我们必须排号,这个就是一个命令模式。 在这个例子里,由于我们的命令(办业务命令、点餐命令)不能马上执行,排号机接受了我们的命令,通过队列等,让我们的命令能保存(封装)下来,以便执行。
定义:一般“行为请求者”与“行为实现者”通常会紧密相连,有时我们需要把他们分离开实现一些功能,而命令模式则将“请求”封装成对象,实现了松耦合。
结构组成及作用
下图是对命令模式定义的uml:
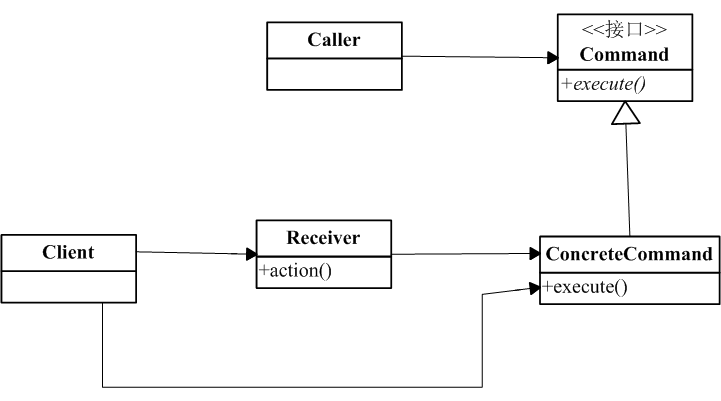
画出类图一目了然,图中command将receiver的action封装起来,以供执行。
示例实现
示例代码模拟电灯开关。
public interface Command {
void execute();
}
实际执行类
/**
* receiver
*/
public class Light {
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("turning on!!!");
}
public void turnOff() {
System.out.println("turning off!!!");
}
}
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
//
// This is the invoker
//
public class Switch {
private Map<String, Command> commandMap = new Hashtable<>();
public void addCommand(final String key, final Command command) {
commandMap.put(key, command);
}
public void executeCommand(String key) {
Command c = commandMap.get(key);
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
c.execute();
}
public void executeAllCommands() {
commandMap.values().stream().forEach(t -> t.execute());
}
}
public class TurnOnCommand implements Command {
private Light light;
public TurnOnCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
light.turnOn();
}
}
public class TurnOffCommand implements Command {
private Light light;
public TurnOffCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
light.turnOff();
}
}
/**
The client
*/
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Switch mySwitch = new Switch();
Light light = new Light();
Command command1 = new TurnOnCommand(light);
Command command2 = new TurnOffCommand(light);
mySwitch.addCommand("turnOn", command1);
mySwitch.addCommand("turnOff", command2);
mySwitch.executeCommand("turnOn");
mySwitch.executeCommand("turnOff");
}
}
java8实现
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Command {
void execute();
}
/**
* receiver
*/
public class Light {
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("turning on!!!");
}
public void turnOff() {
System.out.println("turning off!!!");
}
}
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
//
// This is the invoker
//
public class Switch {
private Map<String, Command> commandMap = new Hashtable<>();
public void addCommand(final String key, final Command command) {
commandMap.put(key, command);
}
public void executeCommand(String key) {
Command c = commandMap.get(key);
Objects.requireNonNull(c);
c.execute();
}
public void executeAllCommands() {
commandMap.values().stream().forEach(t -> t.execute());
}
}
/**
The client
*/
public class Java8TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Switch mySwitch = new Switch();
Light light = new Light();
Command command1 = new TurnOnCommand(light);
Command command2 = new TurnOffCommand(light);
mySwitch.addCommand("turnOn", () -> light.turnOn());
mySwitch.addCommand("turnOff", () -> light.turnOff());
mySwitch.executeCommand("turnOn");
mySwitch.executeCommand("turnOff");
mySwitch.executeAllCommands();
}
}
效果及应用场景
在下面的情况下可以考虑使用命令模式:
- 在不同时刻拍队列、执行请求。也就是说,当使用者希望封装起来的command对象可以与原始“请求”有一个无关的生存期时。
- 希望支持日志和系统恢复。
- 希望支持取消撤销操作。